List To Floor Assertion

The six assertions that you must attend to when auditing occurrence ownership completeness authorization accuracy and cutoff are outlined here occurrence.
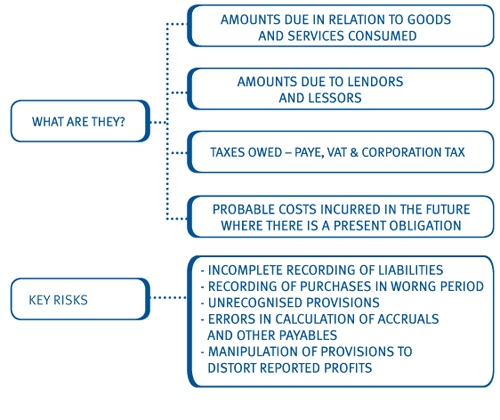
List to floor assertion. The assertion of accuracy and valuation is the statement that all figures presented in a financial statement are accurate and based on proper valuation of assets liabilities and equity balances. During your audit you need to test management financial statement assertions for fixed and intangible asset transactions. For example in order to think you typically begin with what you know to be true the following are illustrative examples of assertions. This assertion is critical for the asset accounts because it is a reflection of the strength of the company.
An assertion is described by an assertion descriptor. In addi tion to the components of every constraint descriptor an assertion. In preparing financial statements management is making implicit or explicit claims i e. Assertions regarding the recognition measurement and presentation of assets liabilities equity income expenses and disclosures in accordance with the applicable financial reporting framework e g.
The auditors test the validity of these assertions by conducting a number of audit tests. To test the occurrence of. Management assertions are claims made by members of management regarding certain aspects of a business. It refers to the fact that the assets the liabilities and the equity balances mentioned in the books exist at the end of the accounting period.
This is a basis for logic thought processes and systems. 4 10 4 assertions an assertion is a named constraint that may relate to the content of individual rows of a table to the entire contents of a table or to a state required to exist among a number of tables. List of audit assertions related to account balances 1 existence. The concept is primarily used in regard to the audit of a company s financial statements where the auditors rely upon a variety of assertions regarding the business.
Occurrence tests whether the fixed asset transactions actually took place. The assertions form a theoretical basis from which external auditors develop a set of audit procedures. All of the information cont. These assertions are as follows.